1900
American surgeon Charles H. Cargile pioneers the use of Cargile membrane in abdominal surgery.
American surgeon Charles H. Cargile pioneers the use of Cargile membrane in abdominal surgery.
During the Second Anglo-Boer War, concentration camps are used by the British to intern Boer women and children. 26,000 prisoners die due to inadequate nutrition, shelter and healthcare.
Blood type classification is introduced by Karl Landsteiner.
The first case of "presenile dementia" - later known as Alzheimer's disease - is diagnosed by Alois Alzheimer.
Henry Dunant, co-founder of Red Cross, is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. The Red Cross itself would receive the same award in 1917.
Foundation of the United States Army Nurse Corps.
New Zealand adopts the Nurses Registration Act, thereby becoming the first country to implement a national register of nurses. The following year, Ellen Dougherty becomes the first registered nurse in the world.
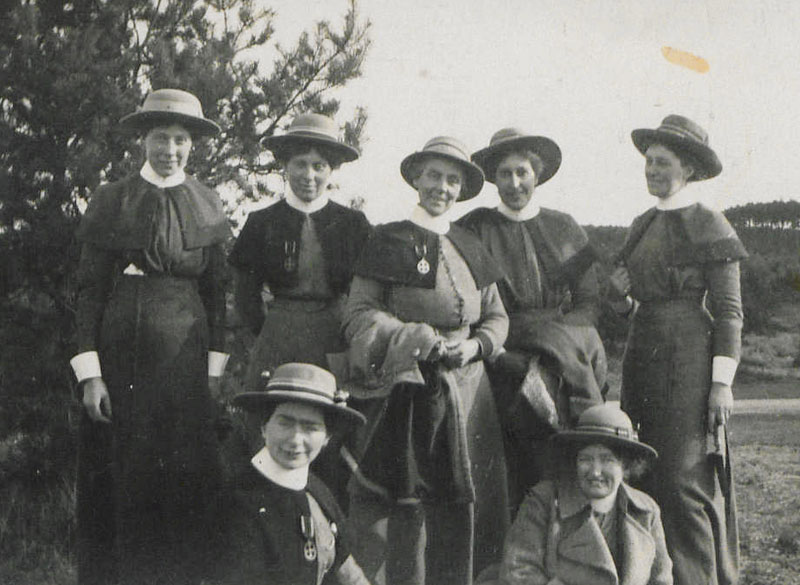

Queen Alexandra's Imperial Military Nursing Service (QAIMNS) is formed in response to the deficiencies in care highlighted during the Second Boer War. The service, which replaces the Army Nursing Service, provides a reserve of nursing staff to support medical services during wartime.
The electrocardiograph (ECG/EKG) is invented by Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven.
The Armstrong Act requiring the official registration of nurses is passed in New York.
A memorial is erected in Arlington National Cemetery in honour of the nurses who served during the Spanish-American War.
Procaine (also known as novocaine) is first synthesised and used as a local anaesthetic.
The Geneva Convention is revised.
The Union Mission Hospital Training School for Nurses is established - the first nurse training school in the Philippines.
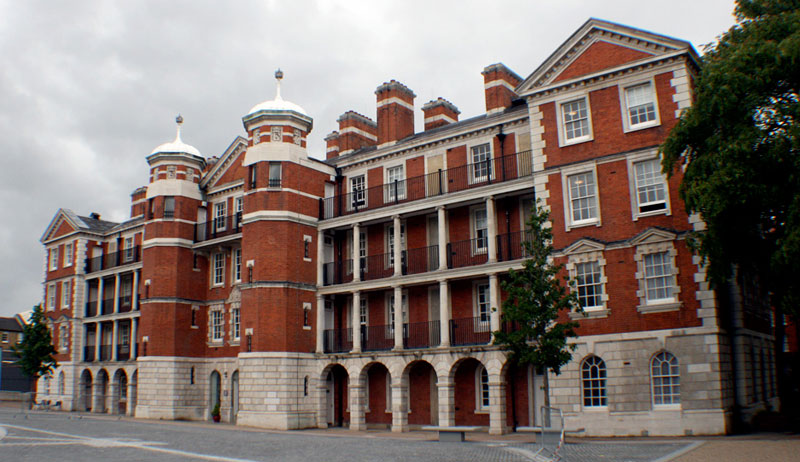

A new medical institution for research and teaching, the Royal Army Medical College, opens at Millbank, London. Research at the College includes a vaccine against typhoid and the development of early gas masks.
Florence Nightingale becomes the first woman to receive the Order of Merit.
The Second Hague Conference results in the signing of an updated Hague Convention.
Establishment of the British voluntary Territorial Force and the Territorial Force Nursing Service.
The stereotactic surgical method, a minimally invasive form of surgery, is invented by British doctors Victor Horsley and Robert H. Clarke.
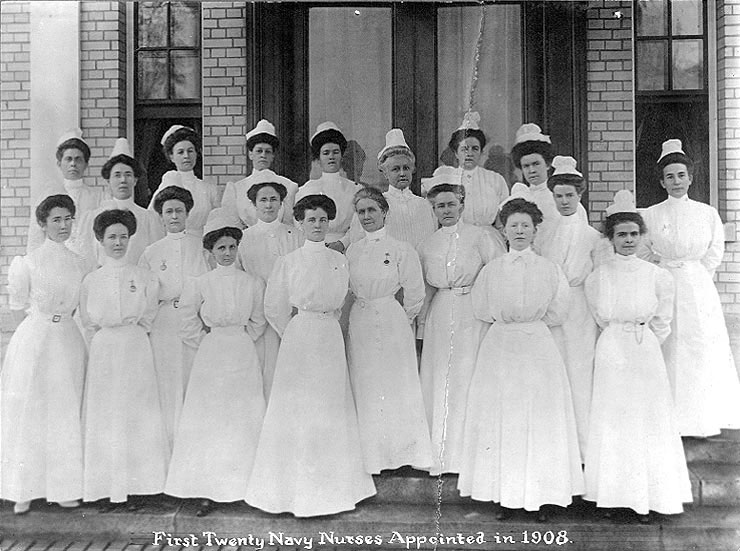

The United States Navy Nurse Corps is established by Act of Congress and the first twenty members, known as the "Sacred Twenty", are selected.
Establishment of the Canadian National Association of Trained Nurses, which would be renamed as the Canadian Nurses Association in 1911.
The American Red Cross Nursing Service is founded, largely thanks to the efforts of the U.S. Army Nurse Corps Superintendent, Jane Arminda Delano.
The first bachelor's degree in nursing is awarded by the University of Minnesota School of Nursing.
The anti-microbial drug arsphenamine is discovered to be an effective treatment for syphilis by Japanese bacteriologist Sahachiro Hata.
French bacteriologist Charles Nicolle identifies lice as the cause of transmission of typhus between humans.
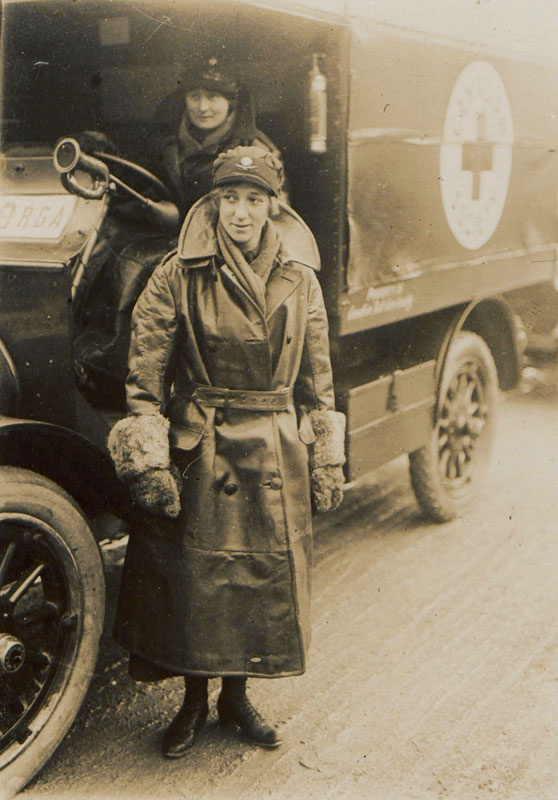

Voluntary Aid Detachments (VADs) - voluntary units providing nursing services in the field - are established in Britain.
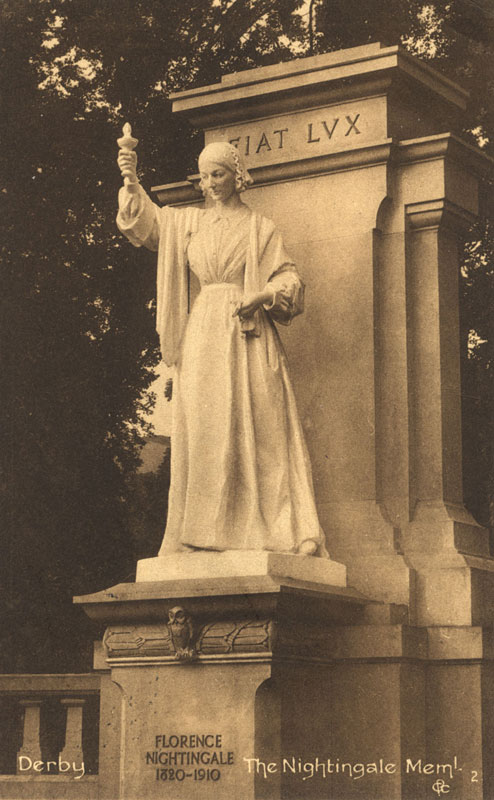

At the age of 90, Florence Nightingale dies on August 13th and is buried at St Margaret at East Wellow, Hampshire.
Henry Dunant, co-founder of the Red Cross, dies in Switzerland at the age of 82.
The first laparoscopic surgical procedure on a human is performed by Swiss physician Hans Christian Jacobaeus.
Following a rigged election, Mexican President Porfirio Díaz is overthrown, resulting in the decade-long Mexican Revolution.
Establishment of the world's first specialised trauma care centre at the University of Louisville Hospital.
Lenah Higbee becomes the second superintendent of the U.S. Navy Nurse Corps. She would become the first female recipient of the Navy Cross in 1918.
In seperate studies, Frederick Hopkins and Casimir Funk propose the existence of vitamins and that they play role in the prevention and cure of some diseases.
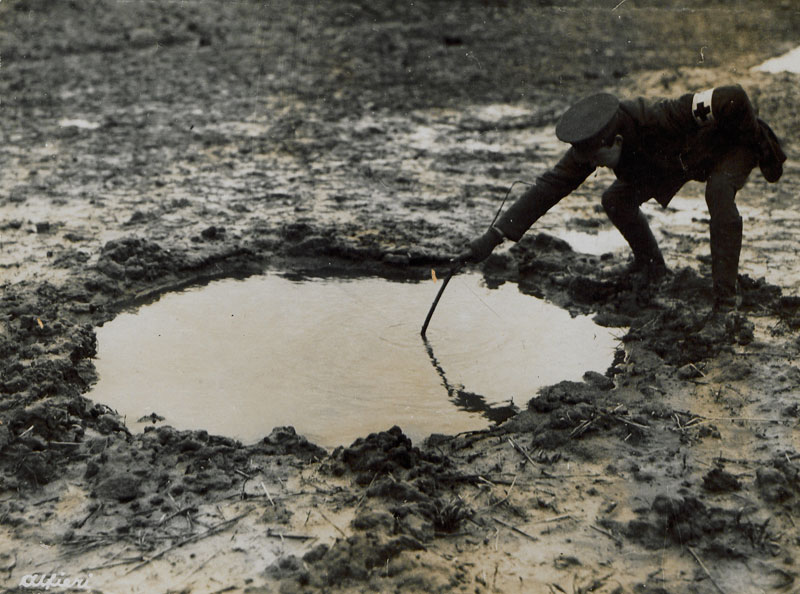

Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia in response to the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo. The event triggers a diplomatic crisis across Europe, culminating in the outbreak of the First World War.
The Australian Red Cross Society is formed, and the British Red Cross establish the Joint War Committee in partnership with the Order of St John.
At the Battle of Neuve Chapelle the Germans fire shells containing a chemical irritant against the French.
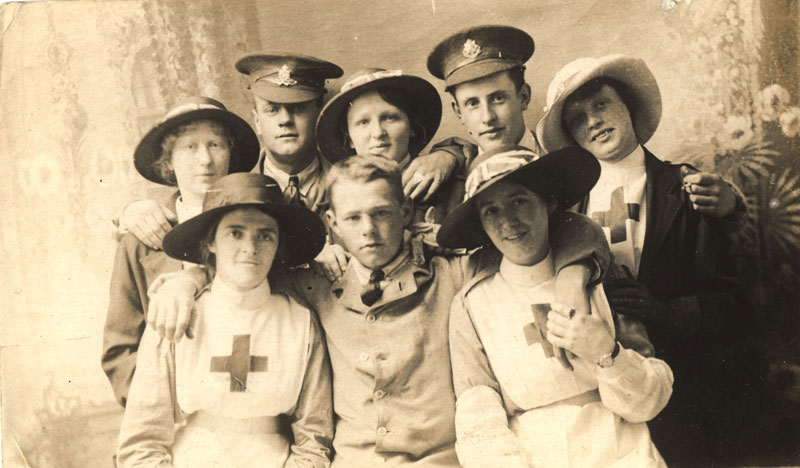

The Red Cross operates on a huge scale during the First World War, providing and supporting vital medical services, sending ICRC delegates to visit prisoners of war and searching for information on captured missing military personnel.
The First Anglo-Belgian Ambulance Unit, later renamed the Friends' Ambulance Unit, is founded by members of the British Religious Society of Friends (the Quakers).
The cold, damp conditions of trench warfare during the First World War lead to an explosion in the number of cases of "trench foot"; the earliest recorded use of the term is in The Lancet in 1915.
Hospital trains are used to evacuate over 100,000 British battlefield casualties from Flanders in a single month.
Italy enters the war on the side of the Entente – Russia, France and Britain.
The Turkish government undertakes a massive programme of deportations and massacres of the Armenian population.
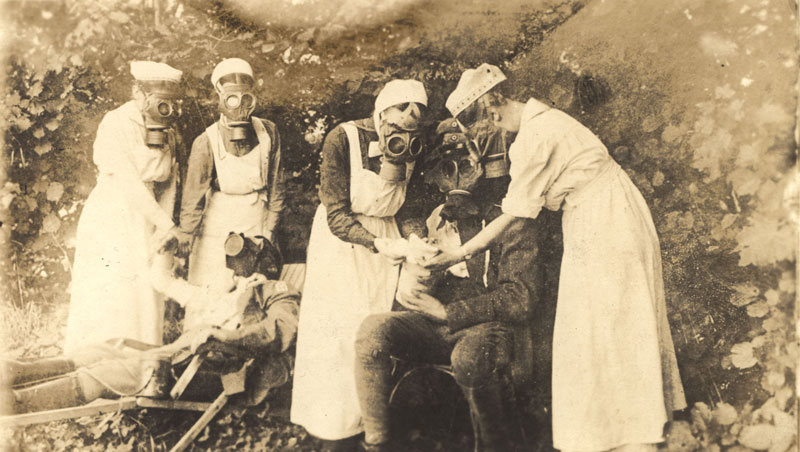

Chlorine gas is used in warfare for the first time by the Germans at the Second Battle of Ypres. The British first use chlorine unsuccessfully at Loos several months later.
British, Anzac and French troops land on the Gallipoli peninsula, Turkey resulting in the loss of 250,000 Allied lives over a period of nine months.
The introduction of a new splint by Robert Jones dramatically reduces soldier deaths from upper leg fractures.
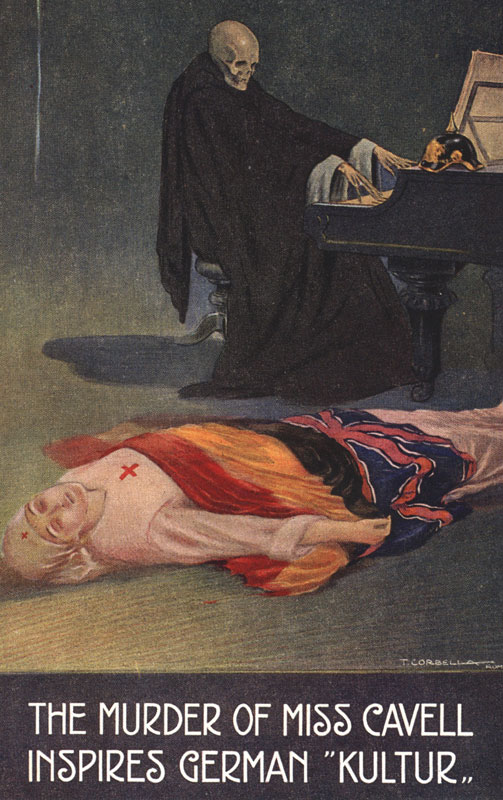

British nurse Edith Cavell is executed by a German firing squad for helping hundreds of Allied soldiers escape to the Netherlands.
Queen Mary Convalescent Auxiliary Hospital is established in Roehampton, London for the treatment and rehabilitation of amputee servicemen. The hospital will have provided 26,000 soldiers with prosthetic limbs by the end of the war.
The Military Service Act in Britain enforces the conscription of men between 18 and 41; the Military Service Act in New Zealand is enacted and the first ballot occurs in November.
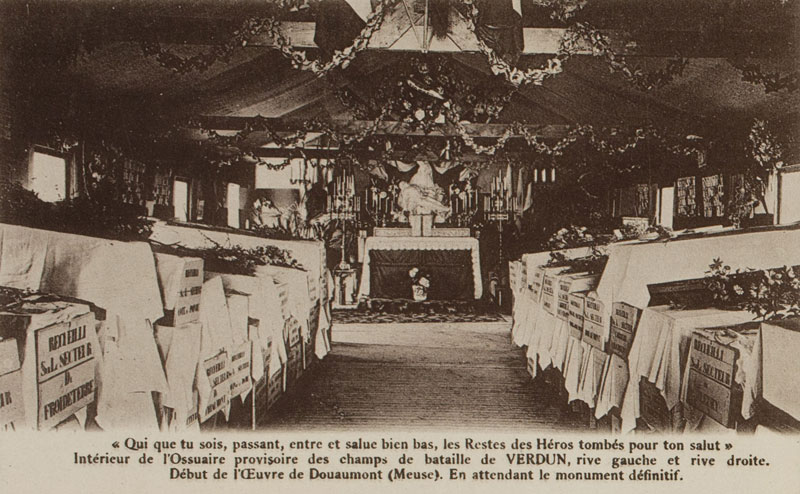

The Germans attack the French at Verdun and the battle, although lasting for nine months, is inconclusive. The Germans lose around 430,000 men and the French around 540,000.
The British and Indian garrison at Kut Al Amara in Mesopotamia surrenders to the Ottomans after a 147-day siege.
The Battle of the Somme results in major casualties but ends inconclusively. The British are the first country to use tanks in battle.
Establishment of the Royal College of Nursing in London.
Alexis Carrel and Henry Drysdale Dakin develop the Carrel-Dakin method for treating combat injuries by irrigating wounds using sodium hypochlorite (known as "Dakin's Solution").
At the request of Queen Mary, the Red Cross convert the Star & Garter Hotel in Richmond, Surrey into a "permanent haven" for disabled servicemen.
The morale of the Russian people collapses due to huge war casualties, inflation and food shortages. This contributes to the political situation and results in the Russian Revolution in 1917.
Germany begins unrestricted U-boat warfare against Allied and neutral shipping, resulting in America declaring war on Germany on 6 April 1917.
Mustard gas is used for the first time by the Germans prior to their defeat of the Entente forces at Passchendaele (the Third Battle of Ypres).
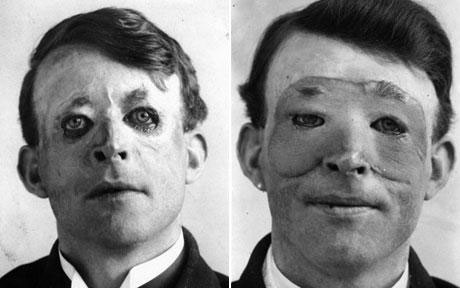
Opening of Queen Mary's Hospital, Sidcup, which pioneers the use of plastic surgery to treat disfigured servicemen. One of its first patients is Walter Yeo, a British naval officer injured in the Battle of Jutland, who is one of the first people in the world to undergo skin flap plastic surgery.
Human blood for transfusion is successfully stored for the first time by the Allies on the battlefields of northern France.
The United States Food Administration is established as an agency for the management of food reserves for the U.S. Army overseas and its allies, under director Herbert Hoover. It is superseded in 1919 by the American Relief Administration, also run by Hoover.
Establishment of the First Home of Recovery in Highfield, Golders Green, London - one of the first medical institutions to treat soldiers affected by "neurasthenia".
Women in Germany and in Britain (aged over 30) are given the right to vote for the first time.

The German Spring Offensive takes place in which German stormtroopers break through the British 5th Army lines. Their advance is halted by the Allies at the Second Battle of the Marne.
Trench fever, first described as a distinct condition in 1915, is identified as a louse-borne disease.
An armistice is signed at Redonthes, France, bringing World War I to an end.
80,000 cases of shell shock are reported to the British Army during the war, with many soldiers continuing to be affected for years. Although recognised as a psychological illness in 1917, the condition is poorly understood, with early treatments including solitary confinement, electroconvulsive therapy and physical re-education.

A devastating influenza pandemic, also known as Spanish Flu, infects 500 million people worldwide, killing between 40 and 100 million.
Frances Reed Elliot becomes the first African–American to be enrolled in the American Red Cross Nursing Service.
Women in the United States gain the right to vote.
The League of Red Cross Societies is formed in the aftermath of the war. It would later be known as the League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (from 1983) and then the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (from 1991).
The British Ministry of Health is formed.
The Turkish War of Independence takes place in response to the partition and occupation of the former Ottoman Empire after the war.
Band-Aid adhesive bandages are invented by American cotton buyer Earle Dickson.
The Royal Army Dental Corps is established in response to the high incidence of face and jaw injuries and dental problems during the First World War.
Spanish military surgeon Fidel Pagés pioneers the application of epidural anaesthesia.
The Anglo-Irish Treaty is signed five years after the Easter Rising of 1916, bringing the Irish War of Independence to an end and leading to the creation of the Irish Free State.
The British government's Report of the War Office Committee of Inquiry into "Shell-Shock" is published. The document outlines approaches for the treatment of shell shock and restricts medical treatment to the severest cases.
The Nurses Registration Act of 1919 becomes effective and Ethel Gordon Fenwick, one of the founders of the BNA and a life-long campaigner for nurse registration, is the first nurse registered in the UK.
Carlos Chagas opens the first Brazilian higher education institution of nursing based on the "Nightingale model" in Rio de Janeiro.
Otto Loewi and Sir Henry Dale describe Acetylcholine, the first known neurotransmitter.
Signing of the Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous or other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare in Geneva.
The first open heart surgical procedure is performed by English surgeon Henry Souttar.

The first effective vaccines for tuberculosis and tetanus are developed.
Alexander Fleming re-discovers penicillin, first identified in 1896, noticing its antibiotic qualities. Fleming publishes his results in early 1929; the first successful recorded treatment utilising penicillin takes place in November 1930.
Philip Drinker and Louis Agassiz Shaw, Jr. develop an effective iron lung, which sees its first clinical use in October.

Two teams of scientists - one led by Albert Szent-Györgyi and Joseph L. Svirbely in Hungary, and another led by Charles Glen King in the United States, identify the anti-scurvy properties of vitamin C. The vitamin is synthesised for the first time in 1933.
The Health Committee of the League of Nations recommends the adoption of the BCG vaccine (first used in 1921) against tuberculosis.
George Papanicolaou announces his discovery that cervical cancer can be identified through the examination of cells gathered from the lining of the vaginal tract, a technique which becomes popularly known as the 'Pap Smear'.

Frank Whittle, an RAF Pilot Officer, submits his first design for a jet engine to superior officers.

Ernest Hemingway publishes his novel, A Farewell to Arms, inspired by his experiences as a Red Cross ambulance driver in Italy during the war.
Adolf Butenandt successfully isolates the hormone oestrogen. Butenandt subsequently isolates progesterone (1934) and testosterone (1935).
Between 24-29 October, share prices on the New York Stock Exchange collapse, in what becomes known as the Wall Street Crash, initiating the Great Depression.
The British Parliament passes the 1929 Local Government Act, under which the remnants of the workhouse system is abolished.

Hans Berger published a paper announcing his development of Electroencephalography (EEG), a method of monitoring the electrical activity of the brain.
The Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War, popularly known as the 1929 Geneva Convention, is signed.
The Hygienic Laboratory of the U.S. Public Health Service is renamed as the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
In January 1930, the Young Plan is agreed, restructuring German reparations for the First World War.
Sergei Yudin performs the first successful transfusion of cadaveric blood (the transfusion of blood from a deceased donor to a living recipient), and establishes the first blood bank at the Nikolay Sklifosovsky Institute.
The First International Congress on Mental Hygiene is held in Washington DC, attended by an estimated 4000 people.
The Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament (alternatively known as the London Naval Treaty) is signed by Britain, France, the United States, Italy and Japan. Under its terms, the major naval powers agreed to restrict the construction of warships, submarines and naval armaments, and to regulate submarine warfare.

A multi-party National Government is formed in the UK under the leadership of Ramsay MacDonald, amidst a financial crisis and a split in his Labour administration. MacDonald is succeeded as Prime Minister by Stanley Baldwin in 1935, and Neville Chamberlain in 1937. Comprised of Conservative, National Labour, National Liberal and independent politicians, the National Governments remain in power until May 1940, when a wartime coalition supported by all of Britain's major parties is formed, with Winston Churchill as Prime Minister.
The Mukden Incident occurs when junior officers of the Japanese Army detonate explosives on the Japanese-owned South Manchurian Railway and blame it on Chinese troops. The incident provides the pretext needed for the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. Further Japanese incursions into, and subsequent occupation of Chinese territory continue prior to the official Japanese declaration of war in 1937.
Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll produce a prototype electron microscope.
The British Parliament passes the Statute of Westminster, establishing the legislative independence of the self-governing Dominions of Canada, New Zealand and Australia in law.
Franklin Delano Roosevelt is elected President of the United States. He secures two further election victories (1936, 1942) before his death in 1945.
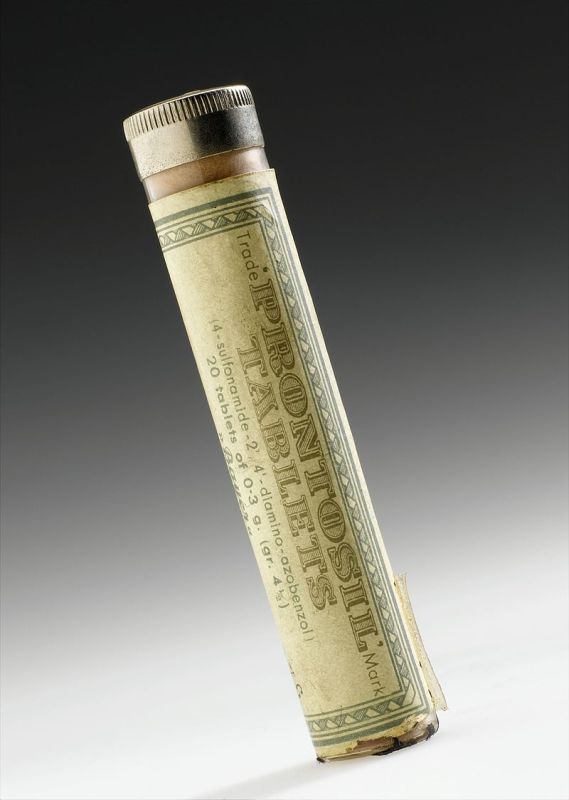

Gerhard Domagk determines that Prontosil, a sulphonamide drug developed by Bayer, is an effective antibiotic.
A team of scientists led by Burrill Bernard Crohn describes what becomes known as Crohn's Disease.
The Chaco War is fought between Bolivia and Paraguay, over disputed territory thought to be rich in oil.
The Tuskegee syphilis experiment, a long-term study in which African-Americans are infected with syphilis and left untreated, without their informed consent, is carried out by the US Public Health Service.
The Conference for the Reduction and Limitation of Armaments (alternatively known as the World Disarmament Conference) is held in Geneva. The German delegation withdraws in October 1933, and the complicated talks ultimately fail to reach any agreement.
The Third International Eugenics Congress is held in New York.
On 30 January, Adolf Hitler is appointed German Chancellor. Subsequent decrees and legislation passed during the coming months, including the Reichstag Fire Decree and Enabling Act form the basis of the Nazi dictatorship.
Wilson Smith, C.H. Andrewes and P. P. Laidlaw isolate the influenza virus.
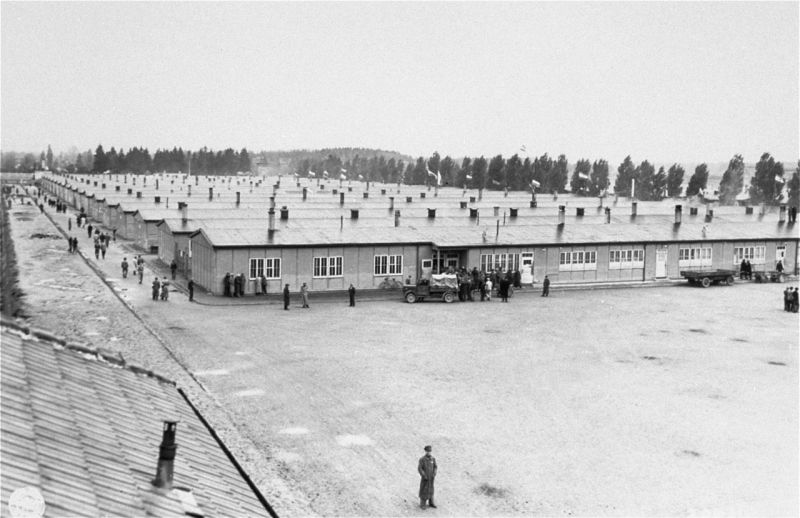

The first concentration camp established by the Nazi regime is founded at Dachau.
Japan withdraws from the League of Nations in March.
Manfred Sakel announces his development of insulin shock therapy (alternatively known as insulin coma therapy), a method of inducing comas to treat mental health conditions and drug addiction.
The American Hospital Association introduced its Blue Cross insurance plan, intended to help US citizens pay for hospital costs.
On 19 October, Germany withdraws from the League of Nations.
On 14 July, the Reichstag passes the Law for the Prevention of Hereditarily Diseased Offspring. Under the terms of the law, those deemed to suffer from a series of disorders faced compulsory sterilisation.
On 29 December, Japan withdraws from the Washington Naval Treaty.
On 8 March, sodium thiopental, the first intravenous anaesthetic to be developed, is administered for the first time at Abbott Laboratories.

Regina Kapeller-Adler develops a chemical pregnancy test.
Benzedrine, the first pharmaceutical amphetamine, is marketed as a decongestant inhaler.
Alcoholics Anonymous is established in the United States by Bill Wilson and Dr Robert Smith.
Ladislas J. Meduna publishes his results into the use of induced seizures to treat schizophrenia, pioneering electroconvulsive therapy.
The first lobotomy, a technique developed by António Egas Moniz, is performed.

The Epidemic Prevention and Water Purification Department of the Kwantung Army, later known as Unit 731, is set up by the Japanese to conduct biological and chemical warfare research. A covert operation, it conducts lethal human experimentation during the Second Sino-Japanese and Second World War. At the end of the Second World War, those involved are captured by the American forces, granted immunity and recruited to work for the U.S biological warfare program. Those captured by the Soviets are tried in War Crime trials in 1949.
On 18 June, the British and German governments sign the Anglo-German Naval Agreement. Under the terms of the Treaty, the tonnage of the German Kriegsmarine is restricted to 35% of that of the Royal Navy.
Between September and November the Reichstag passes the Nuremberg Laws, severely restricting the citizenship and civil rights of Jewish and Romani people in Germany.
Gladys Anderson Emerson isolates vitamin E.
On 28 January, Iceland becomes the first country to legalise abortion on medical grounds.

In October 1935, Italy invades Abyssinia (Ethiopia), initiating the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. Italian forces capture the capital of Addis Ababa in March 1936, but fighting continues into early 1937.
The Saarland is returned to German control after a plebiscite organised by the League of Nations.
The British Parliament passes the Government of India Act, intended to reform the rule of British India through administrative changes and the extension of voting rights.
The first medical textbook written by an African American, Syphilis and Its Treatment is published, having been written by the developer of the ‘Hinton test’ for detecting syphilis, Dr. William Augustus Hinton.
A group of Spanish Generals issue a pronunciamiento, starting the Spanish Civil War. The conflict sees the first widespread use of blood transfusion and mobile operating theatres.
Max Theiler publishes a paper on successful human trials of 17D, an effective yellow fever vaccine.
Legislation signed by President Franklin D. Roosevelt establishes the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
In July, The Marco Polo Bridge Incident marks the start of open hostilities between Japan and China, effectively marking the start of the Second Sino-Japanese War.
The sulphonamide antibiotic M&B 693 is discovered, providing a treatment for pneumonia and many other infections.
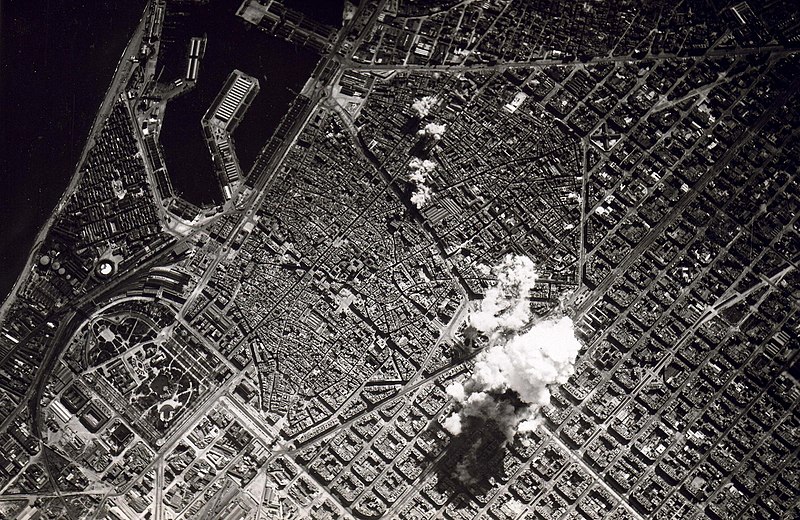

March: Nationalist aircraft bomb the Republican stronghold of Barcelona every two hours for two days. In the aftermath of one raid, the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, receives 300 casualties in 15 minutes.
The Auxiliary Territorial Service, the women's branch of the British Army, is formed. Many of its members will perform tasks related to the provision of medical services, including driving ambulances in the fiercest bombing of the Blitz.
Dr Archibald McIndoe starts work at The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead. McIndoe becomes one of the most renowned plastic surgeons of the Second World War, particularly for his work with burns victims.
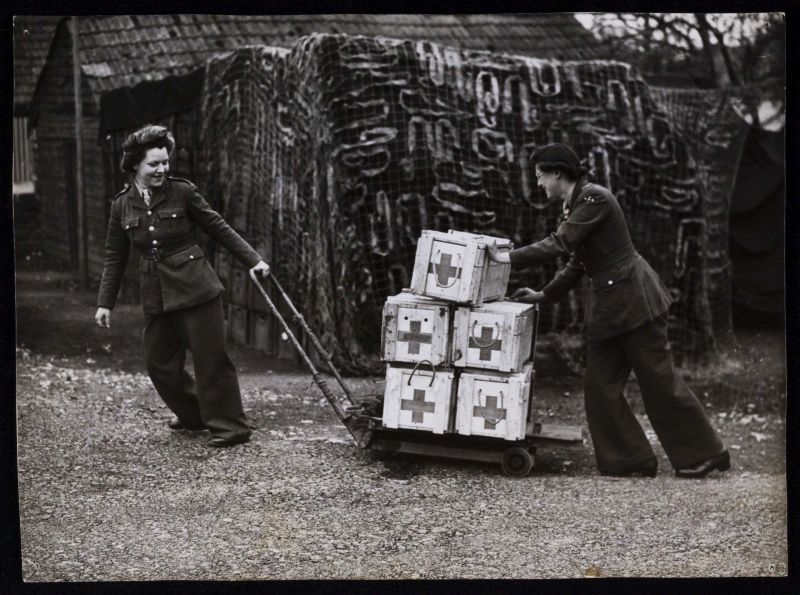

The Army Blood Transfusion Service is established.
The Maudsley Hospital moves to an evacuated school in North London. It is renamed the Mill Hill Emergency Hospital, and the treatment of combat stress is pioneered at the new site.
On 1 September, the German invasion of Poland begins. Great Britain and France declare war on Germany two days later.
During the Battle of France, none of the 17,000 wounded soldiers who have been inoculated against tetanus contract the disease.
An early blood processing program for relief of British war victims, called Plasma for Britain, begins under the direction of Dr. Charles R. Drew.
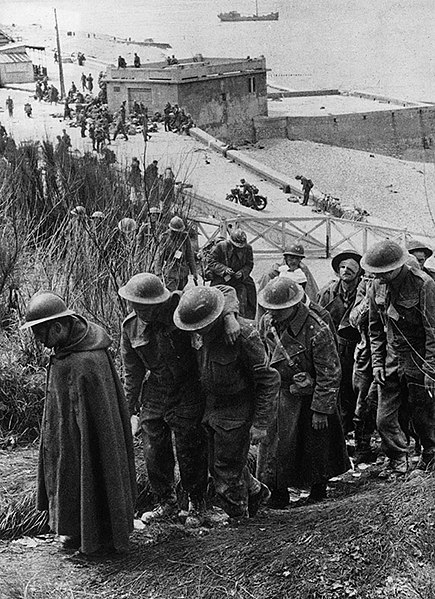

On 2 June, the hospital ship SS Paris is sunk evacuating wounded from Dunkirk. The last allied troops are evacuated on the 4th; the rearguard surrenders soon after.
Between April and July 1940, more than 35 million three-milligram doses of the stimulant Pervitin (a form of methamphetamine) are manufactured for the German armed forces.
15 September: The climax of the Battle of Britain. Over 1500 aircraft take part in an air battle that ultimately persuades Hitler to postpone his planned invasion of Great Britain.
The RAF Hospital at Halton becomes the first hospital to use penicillin on a large scale.
Following political pressure from civil rights groups and the black press, 56 African-American nurses are admitted into the U.S. Army Nurse Corps in 1941, all of whom are sent to segregated bases in the South.
The Lend-Lease Act is enacted in the United States, allowing for supplies to be sold to the United Kingdom and China, to be paid for after the war. The policy is later extended to Free France and the Soviet Union.
Birmingham Accident Hospital opens as the world's first trauma centre.
The 16th Airborne Field Ambulance, the first British field ambulance unit capable of deploying by parachute, is formed.

The Guinea Pig Club is formed by 39 aircrew burns patients, all of whom have gone through multiple surgical procedures.
Operation Barbarossa, the Nazi invasion of the Soviet Union, begins on 22 June.
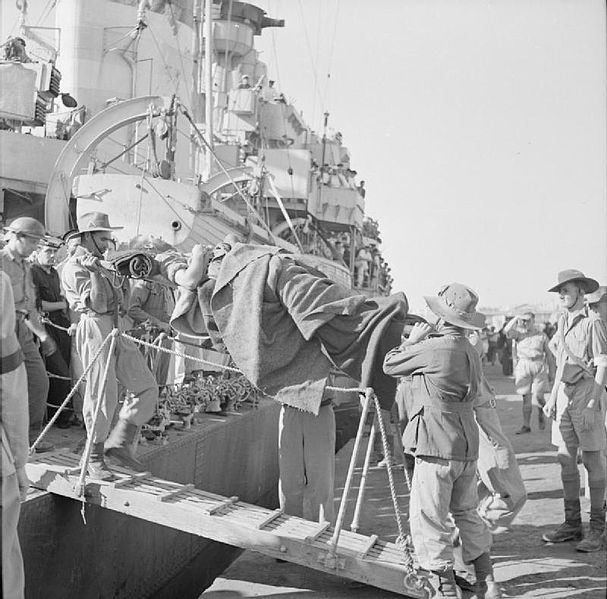

20 May: German paratroopers land on Crete. The ensuing battle lasts for seven days before allied troops withdraw, abandoning the island.
7 December: The Japanese attack Pearl Harbour, prompting the United States' entry into the Second World War.
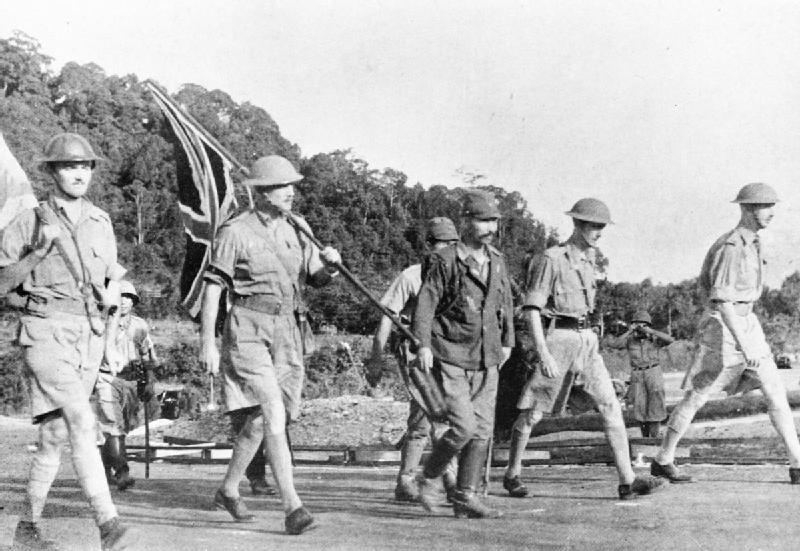

15 February: British forces in Singapore surrender unconditionally to the Japanese. For many, this marks the start of four years in captivity.
9 March: The Dutch East Indies fall to the Japanese, depriving the allies of a major source of the anti-malarial drug quinine.
The Beveridge Report first proposes the idea of a National Health Service in Britain.
47,663 cases of malaria are treated amongst American forces in the Southwest Pacific Area.
The Head of Reich Security, Reinhard Heydrich, is ambushed as he is driven to his headquarters in Prague Castle; he dies of his wounds seven days later.
Doris Miller becomes the first African-American to be awarded the Navy Cross, the third-highest Navy award for gallantry for his ‘extraordinary courage’ during the attack on Pearl Harbour, during which he ‘assisted in moving his Captain, who had been mortally wounded, to a place of greater safety, and later manned and operated a machine gun directed at enemy Japanese attacking aircraft’.
Work commences on the Burma-Thailand railway, utilising 330,000 Allied prisoners of war and civilians as slave labourers. Around a third die from starvation, disease and maltreatment.
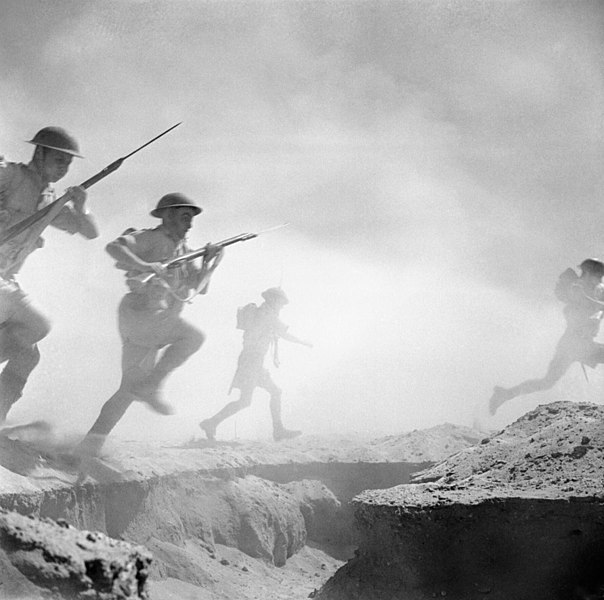

The Second Battle of El Alamein is fought in October and November, culminating in an Allied victory and marking a significant turning point in the North Africa campaign.
While treating victims of the Cocoanut Grove fire in Boston, the clinical staff of the Massachusetts General Hospital demonstrate the efficacy of a new approach to burns treatment, and the value of new blood bank and emergency-response plans.
Severe outbreaks of diphtheria coincide with wartime disruption in Europe. In 1943 alone there are a million cases of diphtheria - 50,000 of which result in death.
Willem J. Kolff, a Dutch doctor, builds the first dialysis machine using empty tin cans and parts from washing machines during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands. Although Kolff's initial prototypes were failures, he eventually develops a functioning machine in the 1950s, in collaboration with colleagues at the Cleveland Clinic.
14-24 January: The Casablanca Conference. Churchill, Roosevelt, Field Marshal Dwight D. Eisenhower, Field Marshal Harold Alexander and others meet to agree on a strategy for the future conduct of the war, concluding that the western allies would launch a joint bomber offensive against Germany, and declare that they were seeking unconditional surrender from Germany, Italy and Japan.
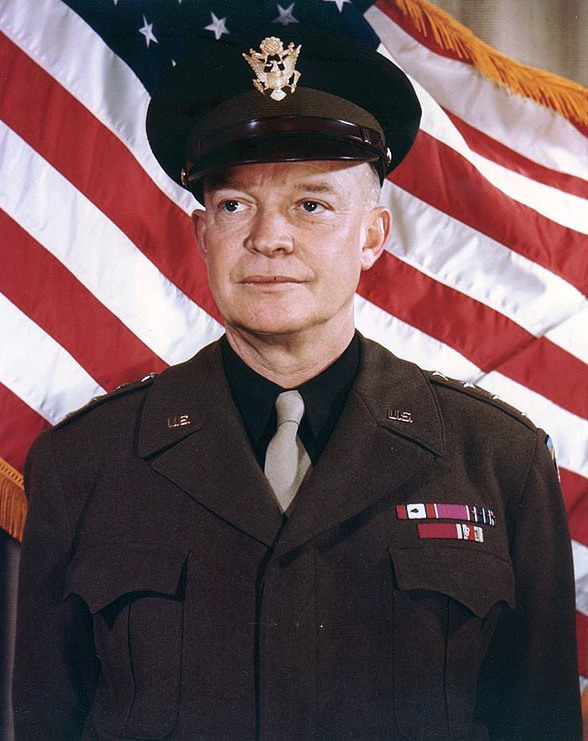

11 February: U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower takes command of the Allied armies in Europe.
14 February - 9 March 1943: The Battle of Medenine (Operation Capri) takes place, culminating in the Axis spoiling attack in Medenine in Tunisia on 6 March.
1-12 March: The Washington Convoy Conference takes place. American, British and Canadian delegates discuss the protection of Atlantic convoys; it is agreed that British and Canadian vessels will assume escort duties previously undertaken by US vessels.
16-17 May: Operation Chastise, or the "Dambusters" raid. A specially-developed "bouncing bomb" is used by the Royal Air Force to breach two dams, leading to the catastrophic flooding of the Ruhr Valley.
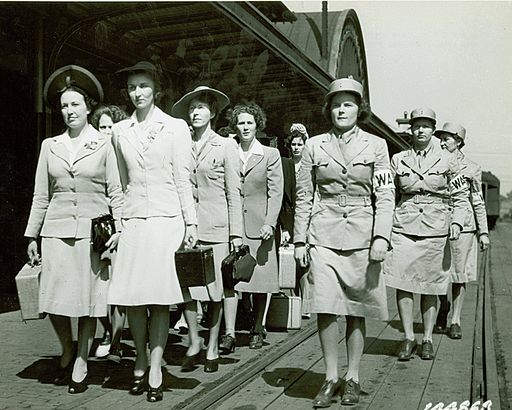

1 July: The Women’s Army Corps (WAC), previously known as the Women's Army Auxiliary Corps (WAAC), begins active duty as a branch of the US Army.
5-16 July: Soviet forces halt the German offensive Operation Citadel during the Battle of Kursk.
25 July: Mussolini is overthrown, arrested by members of his own government, and placed under arrest after the loss of Sicily. An armistice is signed with the Allies on 8 September; in response, German troops occupy northern and central Italy, and establish a puppet government under Mussolini (who is freed from captivity by German special forces.)
5 August: The Women's Flying Training Detachment (WFTD) and the Women's Auxiliary Ferrying Squadron (WAFS) are merged to form the Women Airforce Service Pilots (WASP).
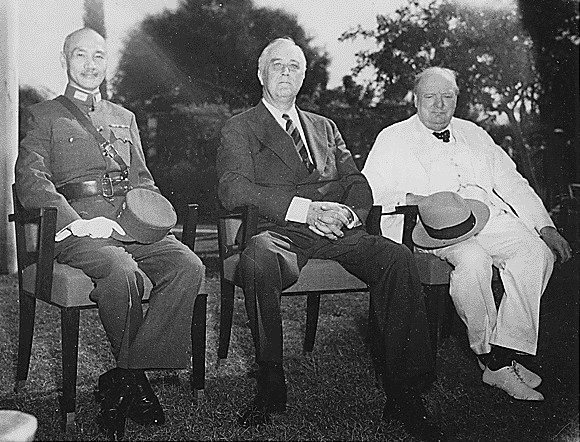

The Cairo Conference takes place in two phases- the first from 23-26 November 1943 and the second from the 3-7 December of the same year. The conference was attended by Churchill, Chiang Kai-Shek and Roosevelt, who discuss operations against Japan and the post-war settlement in Asia; Stalin refuses to attend or send a representative to the conference.
28 November - 1 December: The Teheran Conference takes place and is attended by Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin. The conference marked the first meeting between Stalin and Churchill and saw discussions regarding allied strategy, with a particular focus on the invasion of France and the post-war settlement.
Selman A. Waksman discovers the antibiotic streptomycin, later used to treat tuberculosis.
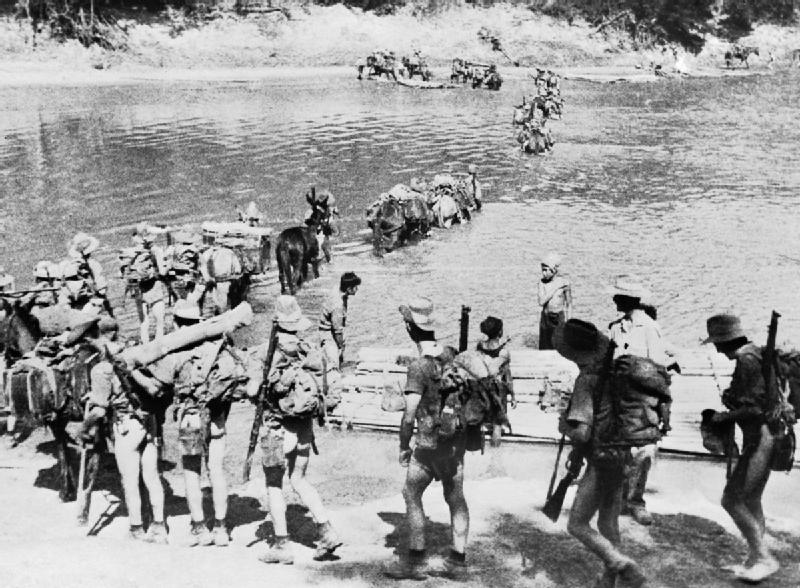

April 1943 - February 1944: Chindit operations in Burma, using long-range penetration and jungle warfare tactics.
David S. Sheridan, a man working in the floor refinishing industry, develops the first disposable catheter, consisting of a hollow plastic tube.
Publication of the White Paper 'A National Health Service' in Britain. The paper highlights the relationship between an improved health service, better management of illness, and a reduced mortality rate.
17 January - 18 May: The Battle of Monte Cassino, a series of four assaults intended to aid an allied advance to Rome, eventually breaks through German lines.
20-25 February: Operation Agreement (otherwise known as "Big Week"), a series of strategic bombing raids carried out against German cities.
15 August - 14 September: Operation Dragoon, the Allied invasion of the French Riviera, forces German forces to evacuate the south of France.

6 June: D-Day or 'Operation Neptune', sees the landing of 24,000 American, British and Canadian troops in German-occupied Normandy.
6 June - 30 August 1944: Operation Overlord, or the Allied invasion of Normandy. The invasion leads to the liberation of the majority of northern France, including Paris, by the end of August.
17 July 1944: The Port Chicago disaster takes place following the explosion of 2,000 tonnes of ammunition which had been loaded onto ships by African-American navy sailors, put under pressure to hurry to load the ammunition as quickly as possible. The explosion resulted in the deaths of 320 military and civilian workers, the majority of whom were black. The event resulted in a mutiny just one month later when fifty African-American sailors refused to carry on loading ammunition under the same precarious working conditions. This led to the first case of a full military trial for a mutiny in US naval history taking place, with the trial being observed by the lawyer Thurgood Marshall. The trial resulted in all of the defendants being convicted and faced criticism in its immediate aftermath for failing to abide by the relevant laws concerning mutiny, leading it to become an influential touchstone within discussions of the desegregation of the navy.
1 August - 2 October 1944: A massive uprising is staged in Warsaw by the Polish Resistance, with the hope of liberating the city with the assistance of the advancing Red Army. The halting of the Soviet advance, coupled with the failure of the Allies to provide sufficient support to the movement, leads to the crushing of the revolt and the deaths of up to 200,000 Polish civilians and Resistance members.

20 October: The Japanese military introduces the Kamikaze suicide plane into service.
The Red Cross is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize.
The ‘golden thirteen’ become the first African-American commissioned naval officers. Samuel L. Gravely, Jr. becomes a commissioned officer in the same year and later goes on to become the first African-American to be put in command of a US warship, as well as the first to be made an admiral.
The Battle of the Bulge, or the Ardennes Counteroffensive, a failed German attempt at pushing the Allied forces back from German home territory, takes place. The battle marks the last major German offensive in the west.
November 1944 - July 1945: The last phase of the Burma Campaign takes place, resulting in the Allied liberation of Burma.
December 1944: During the Battle of the Bulge, General Eisenhower faced being extremely short of replacement troops for existing all-white units and made the decision to allow for 2,000 volunteer African-American servicemen to serve in the segregated platoons, serving under white lieutenants in order to restore numbers within these units. General Eisenhower’s experiment resulted in the platoons serving with distinction and ranking positively in an Army survey conducted the following Summer. The motion was short lived, however, and following the platoons being subjected to racist treatment by white military units whilst serving in occupied Germany, the African-American soldiers were promptly sent back to their previous segregated units for the remainder of the war. Though short lived the experiment would go on to mark an important move towards eventual permanent integration of platoons during the Korean War due to its albeit temporary success.
13-15 February: The German city of Dresden is largely destroyed in a series of Allied air raids.
7 March: Following a sharp rise in the number of wounded American personnel, threats were made of a nursing draft, failing to acknowledge or consider the 9,000 black nurses who had applied to join the Army Nurse Corps. In response to the draft legislation posed, US Congressman Adam Clayton Powell Jr. made an address to the House of Representatives, stating that it was ‘absolutely unbelievable that in times like these, when the world is going forward, that there are leaders in our American life who are going backward’ and laid out his concern that these leaders had “forced our wounded men to face the tragedy of death rather than allow trained nurses to aid because these nurses’ skins happen to be of a different color.”
24 March: The First Allied Airborne Army launches Operation Varsity (part of the British Army’s Operation Plunder), with the aim of breaching the Rhine River and gaining access into northern Germany.
1 April - 22 June: The Battle of Okinawa, the final major military engagement of the Second World War, takes place. Both US and Japanese forces suffer heavy losses.
9 April - 2 May: The Spring Offensive in Italy leads to the unconditional surrender of German forces there.

15 April: British and Canadian troops liberate the Bergen-Belsen concentration camp. Over 13,000 unburied bodies and around 60,000 surviving inmates are found; most of the latter are seriously ill and starving. A team from the British Red Cross are sent to Belsen to lead relief efforts.
30 April: Adolf Hitler commits suicide in his Berlin bunker.
April: 1,500,000 German prisoners are captured by Allied troops on the Western Front.
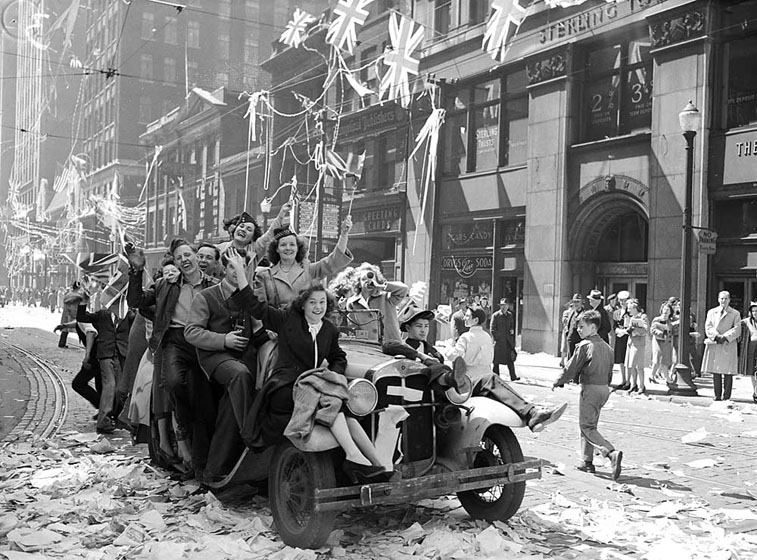

In the early hours of 7 May, the German government signs an unconditional surrender, officially ratified on 8 May - which is celebrated as VE (Victory in Europe) Day by the western allies. An instrument of surrender is signed in Berlin on 9 May (celebrated as Victory Day in Russia.)
5 June: The signing of the Berlin Declaration, under which the Allied Powers assume "supreme authority" over occupied Germany.
18 June: The demobilisation of British forces begins, leading to the release of 4.3 million servicemen and women over the course of the following eighteen months.
25 June: The UN Charter is signed in San Francisco, formally establishing the United Nations.
June 1945: The tetanus toxoid vaccine is made available for civilian use.
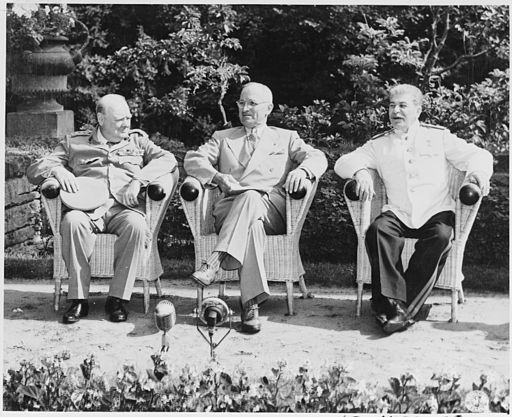

17 July - 2 August: The Potsdam Conference is held in Germany. During the conference the terms of Japan's surrender are agreed, peace treaties are drawn up, reparations for Germany are discussed, and the decision to hold war trials is made.
6 & 9 August: Atomic bombs are dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki by the United States.
15 August: Japan surrenders to the allies.
18 August: The American Red Cross ends its wartime blood programme for the military, having collected more than 13 million pints of blood.
A tetravalent pneumococcal vaccine, created with four pneumococcus types, is introduced. However, owing to the widespread adoption of penicillin to treat pneumococcal infections, the vaccine does not gain much traction.
The first vaccine for influenza is introduced, initially for military use.

20 November 1945 - 1 October 1946: The International Military Tribunal opens in Nuremberg in order to prosecute surviving members of the Nazi administration for charges of crimes against humanity. The trials reach a conclusion with the condemnation of eleven men found guilty of crimes against humanity. Ten of these men are executed on 16 October, with Hermann Göring having committed suicide in his cell the night before.
July: The first issue of the Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery is published, providing a forum for the dissemination of knowledge and discoveries among plastic surgeons and other clinicians.
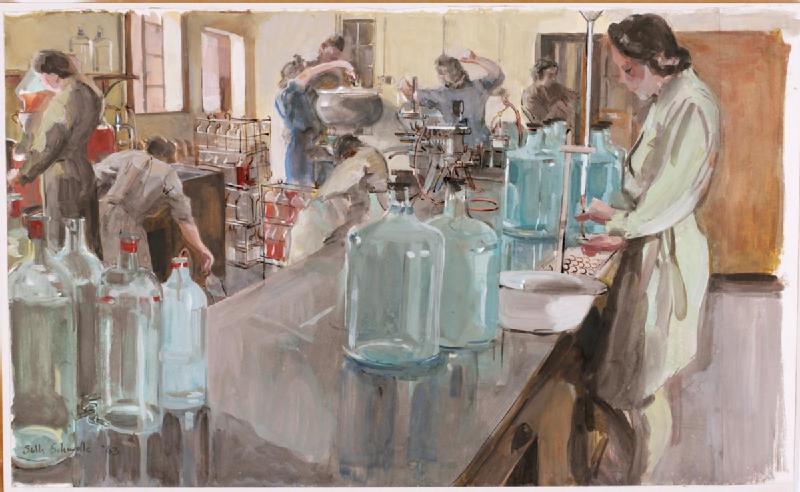

September: The British Army Blood Supply Depot is merged with the Emergency Medical Service's regional depots to form the National Blood Transfusion Service of England and Wales.
November: The National Health Service Act 1946 is passed by the British Parliament, intended to create a comprehensive health service for England and Wales.
A Cleveland cardiovascular surgeon, Claude Beck, successfully defibrillates the heart of a 14-year-old boy during cardiac surgery, marking the first successful clinical application of defibrillation.
British India becomes independent and is partitioned into two states, India and Pakistan.
7 April: The World Health Organisation, an agency of the United Nations, begins operations.
On 24 June 1948 the Berlin Blockade begins. In a bid to maintain control of currency in the Russian-occupied zone of Berlin, the Soviet authorities cut road, rail and canal access to the French, British and American-occupied sectors of the city. In response, the western allies initiate the Berlin Airlift, flying thousands of tonnes of supplies in to West Berlin daily. The blockade is lifted on 12 May 1949.

5 July: The National Health Service (NHS), founded to provide healthcare services available to all regardless of wealth or standing, begins operations in Britain.
1 August: The adoption of the Fourth Geneva Convention, which establishes guidelines for the protection of civilians in a war zone, is signed.
1 October: George C. Marshall is appointed President of the American Red Cross.
The World Health Organization publishes ICD-6, the sixth revision of the International statistical classification of diseases, the first to include a section on mental health conditions.
John Enders, Thomas Weller and Frederick Robbins successfully grow poliovirus in culture, paving the way for polio vaccines. Their technique is later used in the production of vaccines against measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox.
Doctors at Robert Breck Brigham Hospital become the first to administer cortisone, a steroid treatment, to patients with rheumatoid arthritis.