1900
American surgeon Charles H. Cargile pioneers the use of Cargile membrane in abdominal surgery.
American surgeon Charles H. Cargile pioneers the use of Cargile membrane in abdominal surgery.
During the Second Anglo-Boer War, concentration camps are used by the British to intern Boer women and children. 26,000 prisoners die due to inadequate nutrition, shelter and healthcare.
Blood type classification is introduced by Karl Landsteiner.
The first case of "presenile dementia" - later known as Alzheimer's disease - is diagnosed by Alois Alzheimer.
Henry Dunant, co-founder of Red Cross, is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. The Red Cross itself would receive the same award in 1917.
Foundation of the United States Army Nurse Corps.
New Zealand adopts the Nurses Registration Act, thereby becoming the first country to implement a national register of nurses. The following year, Ellen Dougherty becomes the first registered nurse in the world.
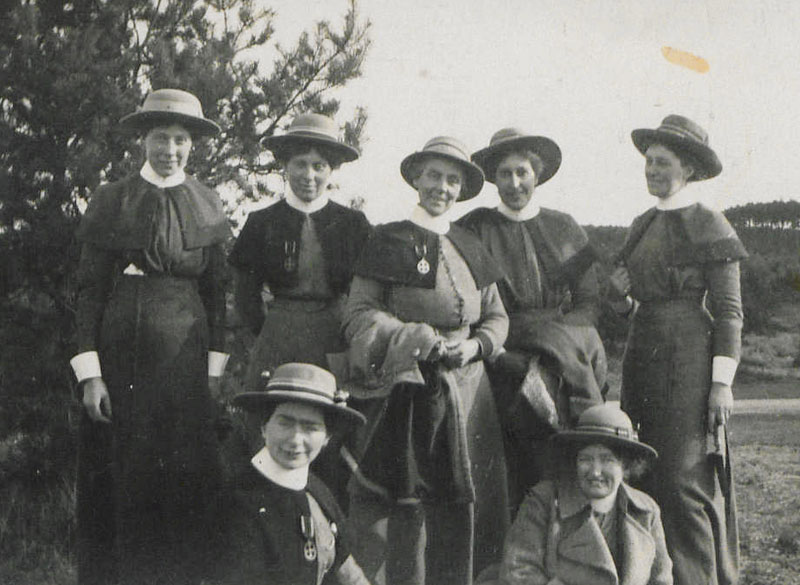

Queen Alexandra's Imperial Military Nursing Service (QAIMNS) is formed in response to the deficiencies in care highlighted during the Second Boer War. The service, which replaces the Army Nursing Service, provides a reserve of nursing staff to support medical services during wartime.
The electrocardiograph (ECG/EKG) is invented by Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven.
The Armstrong Act requiring the official registration of nurses is passed in New York.
A memorial is erected in Arlington National Cemetery in honour of the nurses who served during the Spanish-American War.
Procaine (also known as novocaine) is first synthesised and used as a local anaesthetic.
The Geneva Convention is revised.
The Union Mission Hospital Training School for Nurses is established - the first nurse training school in the Philippines.
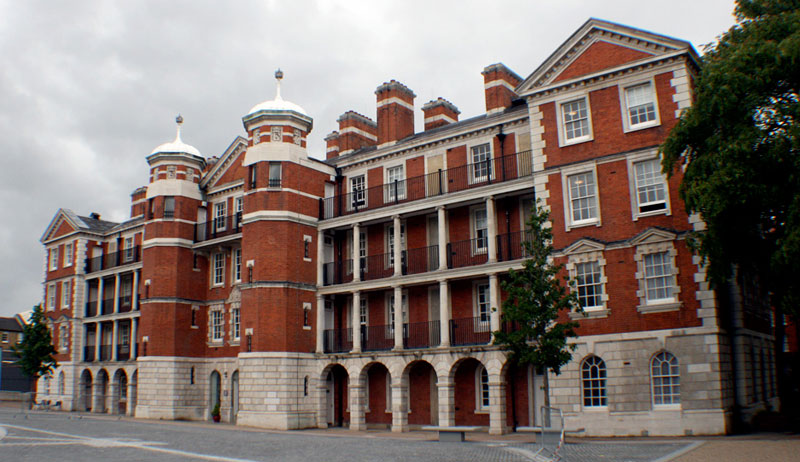

A new medical institution for research and teaching, the Royal Army Medical College, opens at Millbank, London. Research at the College includes a vaccine against typhoid and the development of early gas masks.
Florence Nightingale becomes the first woman to receive the Order of Merit.
The Second Hague Conference results in the signing of an updated Hague Convention.
Establishment of the British voluntary Territorial Force and the Territorial Force Nursing Service.
The stereotactic surgical method, a minimally invasive form of surgery, is invented by British doctors Victor Horsley and Robert H. Clarke.
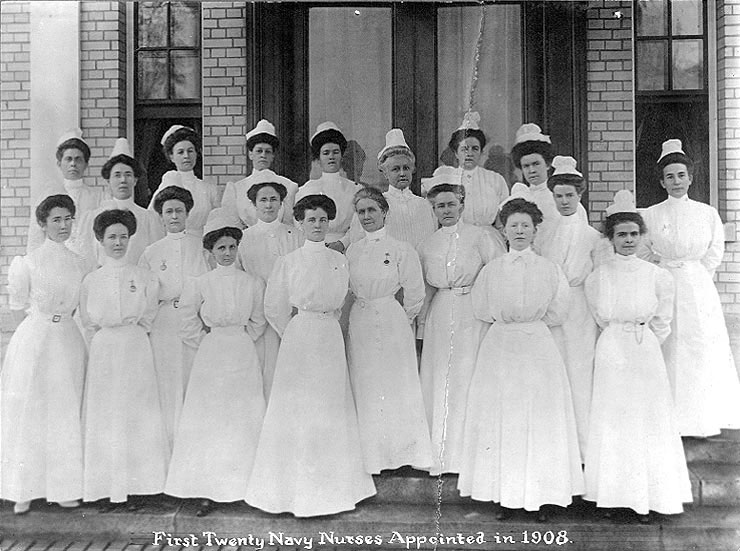

The United States Navy Nurse Corps is established by Act of Congress and the first twenty members, known as the "Sacred Twenty", are selected.
Establishment of the Canadian National Association of Trained Nurses, which would be renamed as the Canadian Nurses Association in 1911.
The American Red Cross Nursing Service is founded, largely thanks to the efforts of the U.S. Army Nurse Corps Superintendent, Jane Arminda Delano.
The first bachelor's degree in nursing is awarded by the University of Minnesota School of Nursing.
The anti-microbial drug arsphenamine is discovered to be an effective treatment for syphilis by Japanese bacteriologist Sahachiro Hata.
French bacteriologist Charles Nicolle identifies lice as the cause of transmission of typhus between humans.
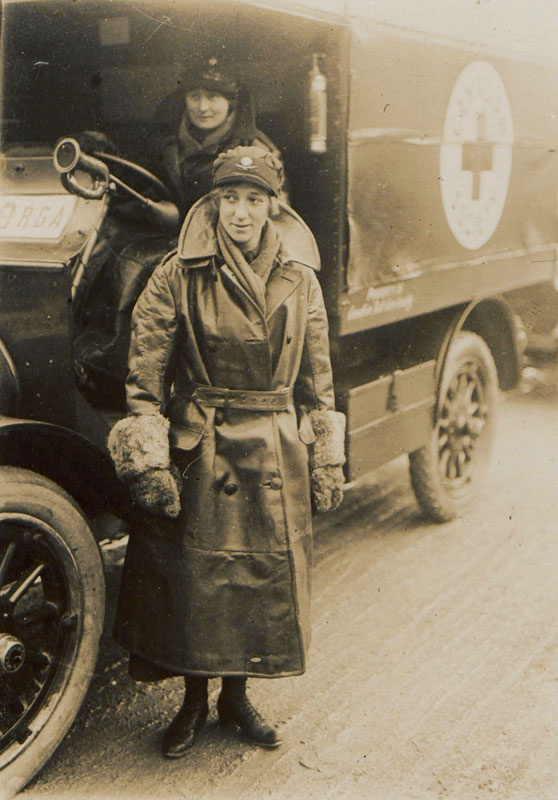

Voluntary Aid Detachments (VADs) - voluntary units providing nursing services in the field - are established in Britain.
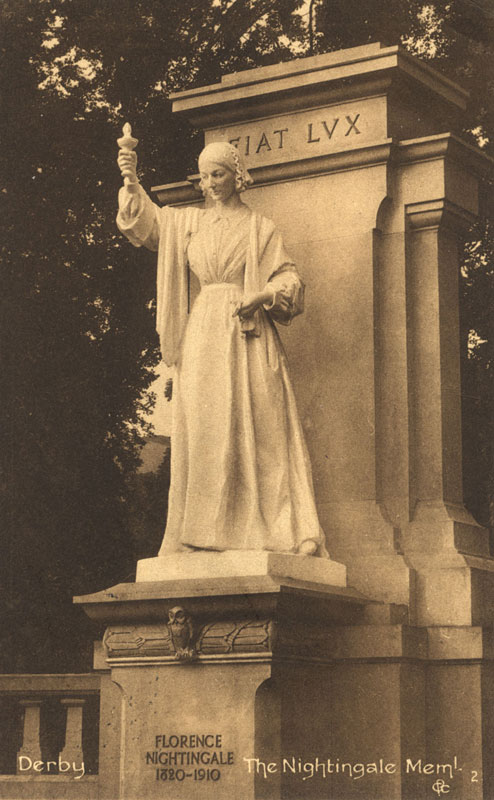

At the age of 90, Florence Nightingale dies on August 13th and is buried at St Margaret at East Wellow, Hampshire.
Henry Dunant, co-founder of the Red Cross, dies in Switzerland at the age of 82.
The first laparoscopic surgical procedure on a human is performed by Swiss physician Hans Christian Jacobaeus.
Following a rigged election, Mexican President Porfirio Díaz is overthrown, resulting in the decade-long Mexican Revolution.
Establishment of the world's first specialised trauma care centre at the University of Louisville Hospital.
Lenah Higbee becomes the second superintendent of the U.S. Navy Nurse Corps. She would become the first female recipient of the Navy Cross in 1918.
In seperate studies, Frederick Hopkins and Casimir Funk propose the existence of vitamins and that they play role in the prevention and cure of some diseases.
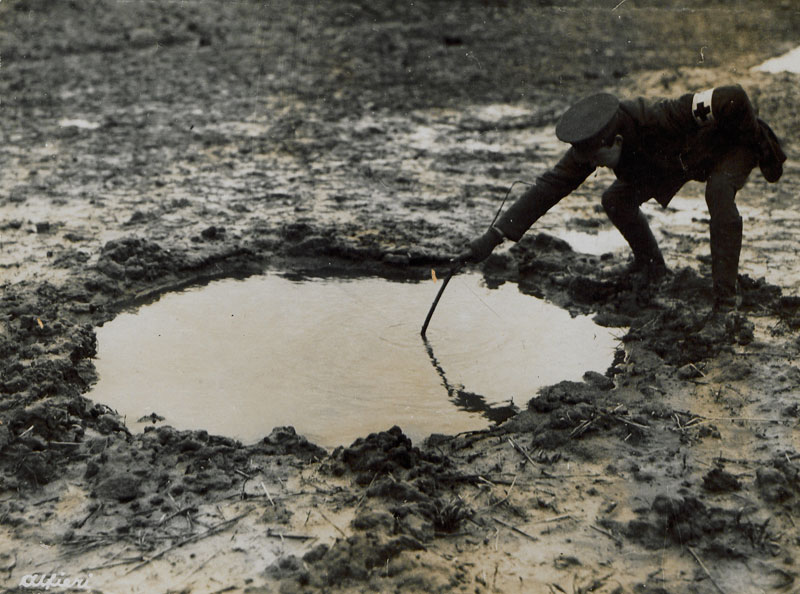

Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia in response to the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo. The event triggers a diplomatic crisis across Europe, culminating in the outbreak of the First World War.
The Australian Red Cross Society is formed, and the British Red Cross establish the Joint War Committee in partnership with the Order of St John.
At the Battle of Neuve Chapelle the Germans fire shells containing a chemical irritant against the French.
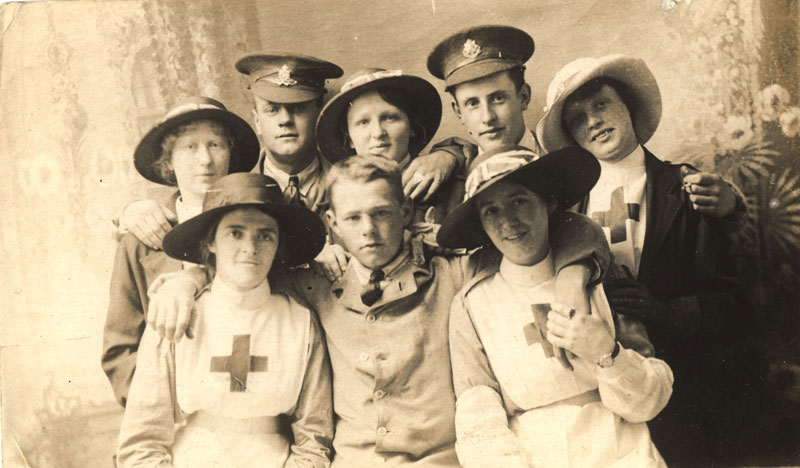

The Red Cross operates on a huge scale during the First World War, providing and supporting vital medical services, sending ICRC delegates to visit prisoners of war and searching for information on captured missing military personnel.
The First Anglo-Belgian Ambulance Unit, later renamed the Friends' Ambulance Unit, is founded by members of the British Religious Society of Friends (the Quakers).
The cold, damp conditions of trench warfare during the First World War lead to an explosion in the number of cases of "trench foot"; the earliest recorded use of the term is in The Lancet in 1915.
Hospital trains are used to evacuate over 100,000 British battlefield casualties from Flanders in a single month.
Italy enters the war on the side of the Entente – Russia, France and Britain.
The Turkish government undertakes a massive programme of deportations and massacres of the Armenian population.
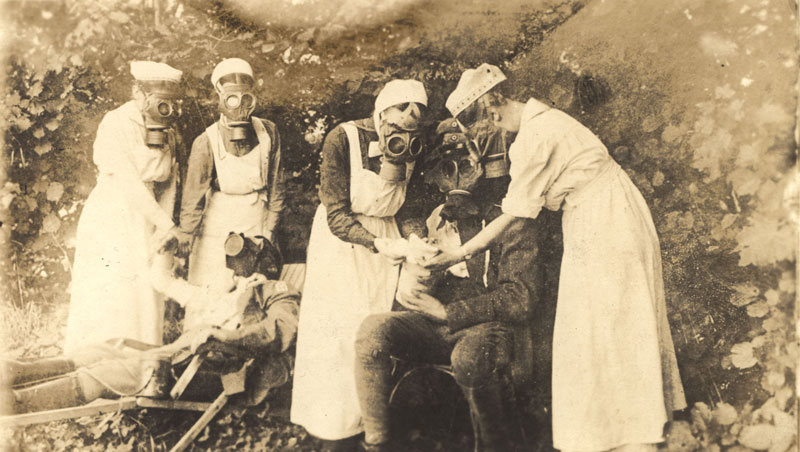

Chlorine gas is used in warfare for the first time by the Germans at the Second Battle of Ypres. The British first use chlorine unsuccessfully at Loos several months later.
British, Anzac and French troops land on the Gallipoli peninsula, Turkey resulting in the loss of 250,000 Allied lives over a period of nine months.
The introduction of a new splint by Robert Jones dramatically reduces soldier deaths from upper leg fractures.
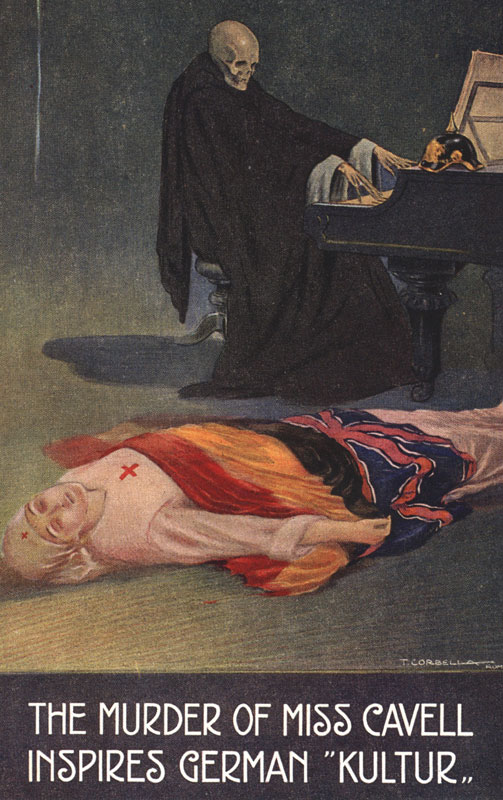

British nurse Edith Cavell is executed by a German firing squad for helping hundreds of Allied soldiers escape to the Netherlands.
Queen Mary Convalescent Auxiliary Hospital is established in Roehampton, London for the treatment and rehabilitation of amputee servicemen. The hospital will have provided 26,000 soldiers with prosthetic limbs by the end of the war.
The Military Service Act in Britain enforces the conscription of men between 18 and 41; the Military Service Act in New Zealand is enacted and the first ballot occurs in November.
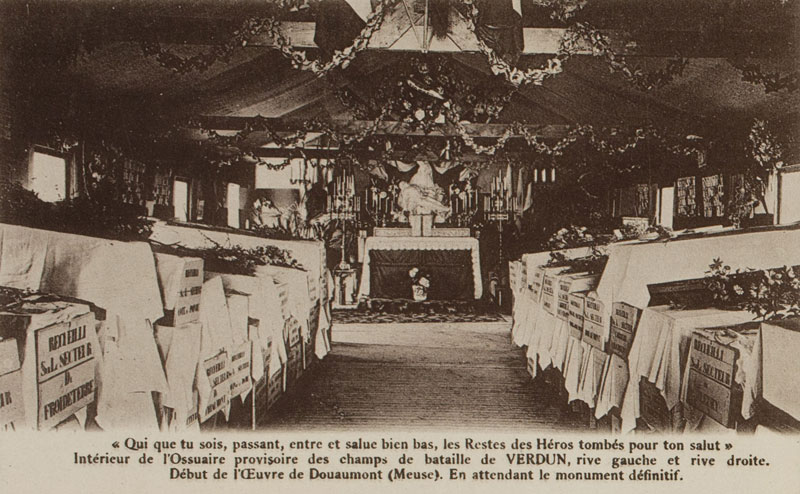

The Germans attack the French at Verdun and the battle, although lasting for nine months, is inconclusive. The Germans lose around 430,000 men and the French around 540,000.
The British and Indian garrison at Kut Al Amara in Mesopotamia surrenders to the Ottomans after a 147-day siege.
The Battle of the Somme results in major casualties but ends inconclusively. The British are the first country to use tanks in battle.
Establishment of the Royal College of Nursing in London.
Alexis Carrel and Henry Drysdale Dakin develop the Carrel-Dakin method for treating combat injuries by irrigating wounds using sodium hypochlorite (known as "Dakin's Solution").
At the request of Queen Mary, the Red Cross convert the Star & Garter Hotel in Richmond, Surrey into a "permanent haven" for disabled servicemen.
The morale of the Russian people collapses due to huge war casualties, inflation and food shortages. This contributes to the political situation and results in the Russian Revolution in 1917.
Germany begins unrestricted U-boat warfare against Allied and neutral shipping, resulting in America declaring war on Germany on 6 April 1917.
Mustard gas is used for the first time by the Germans prior to their defeat of the Entente forces at Passchendaele (the Third Battle of Ypres).
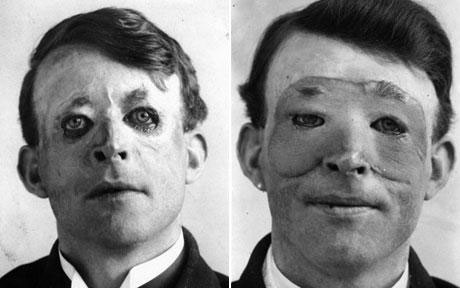
Opening of Queen Mary's Hospital, Sidcup, which pioneers the use of plastic surgery to treat disfigured servicemen. One of its first patients is Walter Yeo, a British naval officer injured in the Battle of Jutland, who is one of the first people in the world to undergo skin flap plastic surgery.
Human blood for transfusion is successfully stored for the first time by the Allies on the battlefields of northern France.
The United States Food Administration is established as an agency for the management of food reserves for the U.S. Army overseas and its allies, under director Herbert Hoover. It is superseded in 1919 by the American Relief Administration, also run by Hoover.
Establishment of the First Home of Recovery in Highfield, Golders Green, London - one of the first medical institutions to treat soldiers affected by "neurasthenia".
Women in Germany and in Britain (aged over 30) are given the right to vote for the first time.

The German Spring Offensive takes place in which German stormtroopers break through the British 5th Army lines. Their advance is halted by the Allies at the Second Battle of the Marne.
Trench fever, first described as a distinct condition in 1915, is identified as a louse-borne disease.
An armistice is signed at Redonthes, France, bringing World War I to an end.
80,000 cases of shell shock are reported to the British Army during the war, with many soldiers continuing to be affected for years. Although recognised as a psychological illness in 1917, the condition is poorly understood, with early treatments including solitary confinement, electroconvulsive therapy and physical re-education.

A devastating influenza pandemic, also known as Spanish Flu, infects 500 million people worldwide, killing between 40 and 100 million.
Frances Reed Elliot becomes the first African–American to be enrolled in the American Red Cross Nursing Service.
Women in the United States gain the right to vote.
The League of Red Cross Societies is formed in the aftermath of the war. It would later be known as the League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (from 1983) and then the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (from 1991).
The British Ministry of Health is formed.
The Turkish War of Independence takes place in response to the partition and occupation of the former Ottoman Empire after the war.
Band-Aid adhesive bandages are invented by American cotton buyer Earle Dickson.
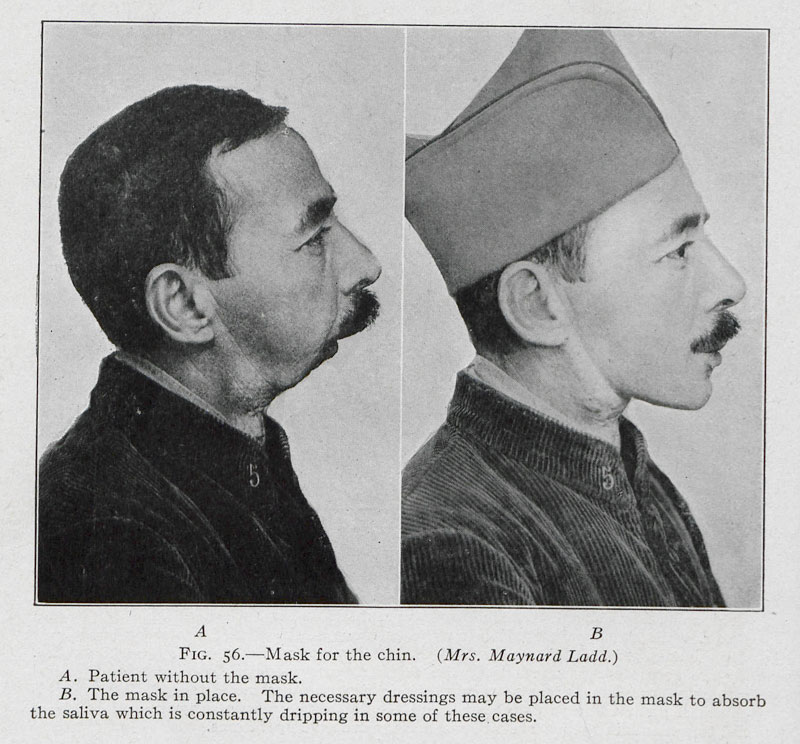
The Royal Army Dental Corps is established in response to the high incidence of face and jaw injuries and dental problems during the First World War.
Spanish military surgeon Fidel Pagés pioneers the application of epidural anaesthesia.
The Anglo-Irish Treaty is signed five years after the Easter Rising of 1916, bringing the Irish War of Independence to an end and leading to the creation of the Irish Free State.
The British government's Report of the War Office Committee of Inquiry into "Shell-Shock" is published. The document outlines approaches for the treatment of shell shock and restricts medical treatment to the severest cases.
The Nurses Registration Act of 1919 becomes effective and Ethel Gordon Fenwick, one of the founders of the BNA and a life-long campaigner for nurse registration, is the first nurse registered in the UK.
Carlos Chagas opens the first Brazilian higher education institution of nursing based on the "Nightingale model" in Rio de Janeiro.
Otto Loewi and Sir Henry Dale describe Acetylcholine, the first known neurotransmitter.
Signing of the Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous or other Gases, and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare in Geneva.
The first open heart surgical procedure is performed by English surgeon Henry Souttar.

The first effective vaccines for tuberculosis and tetanus are developed.
Alexander Fleming re-discovers penicillin, first identified in 1896, noticing its antibiotic qualities. Fleming publishes his results in early 1929; the first successful recorded treatment utilising penicillin takes place in November 1930.
Philip Drinker and Louis Agassiz Shaw, Jr. develop an effective iron lung, which sees its first clinical use in October.

Two teams of scientists - one led by Albert Szent-Györgyi and Joseph L. Svirbely in Hungary, and another led by Charles Glen King in the United States, identify the anti-scurvy properties of vitamin C. The vitamin is synthesised for the first time in 1933.
The Health Committee of the League of Nations recommends the adoption of the BCG vaccine (first used in 1921) against tuberculosis.
George Papanicolaou announces his discovery that cervical cancer can be identified through the examination of cells gathered from the lining of the vaginal tract, a technique which becomes popularly known as the 'Pap Smear'.

Frank Whittle, an RAF Pilot Officer, submits his first design for a jet engine to superior officers.

Ernest Hemingway publishes his novel, A Farewell to Arms, inspired by his experiences as a Red Cross ambulance driver in Italy during the war.
Adolf Butenandt successfully isolates the hormone oestrogen. Butenandt subsequently isolates progesterone (1934) and testosterone (1935).
Between 24-29 October, share prices on the New York Stock Exchange collapse, in what becomes known as the Wall Street Crash, initiating the Great Depression.
The British Parliament passes the 1929 Local Government Act, under which the remnants of the workhouse system is abolished.

Hans Berger published a paper announcing his development of Electroencephalography (EEG), a method of monitoring the electrical activity of the brain.
The Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War, popularly known as the 1929 Geneva Convention, is signed.
The Hygienic Laboratory of the U.S. Public Health Service is renamed as the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
In January 1930, the Young Plan is agreed, restructuring German reparations for the First World War.
Sergei Yudin performs the first successful transfusion of cadaveric blood (the transfusion of blood from a deceased donor to a living recipient), and establishes the first blood bank at the Nikolay Sklifosovsky Institute.
The First International Congress on Mental Hygiene is held in Washington DC, attended by an estimated 4000 people.
The Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament (alternatively known as the London Naval Treaty) is signed by Britain, France, the United States, Italy and Japan. Under its terms, the major naval powers agreed to restrict the construction of warships, submarines and naval armaments, and to regulate submarine warfare.